Set up HTTP callbacks
Chat supports HTTP callbacks (webhooks). After you set up HTTP callbacks for your Chat app, the Chat server sends notifications in the form of HTTP POST requests to your app server when specified events occur.
You can use the HTTP callbacks to synchronize messages on your own server, or moderate message content.
Understand the tech
According to whether the message delivery is intervened, the callbacks are divided in two categories:
- Pre-delivery callbacks: Mainly used for content moderation. When the Chat server receives a message from the client app, it sends a request to your app server and waits for a response that decides if the message delivery is passed or rejected. Pre-delivery callbacks only apply to messages sent from your client apps.
- Post-delivery callbacks: Mainly used for data synchronization. When certain events occur, for example, a user sends out a message or gets offline, the Chat server sends a request to your app server and does not validate the response content. Post-delivery callbacks apply to messages and other events sent from you client and server apps.
The following table summarizes the differences between the two categories of callbacks.
| Category | Pre-delivery callback | Post-delivery callback |
|---|---|---|
| Supported platforms | Client SDKs | Client SDKs and REST APIs |
| Supported events | Only messages | Messages and other events |
| Response required | Yes | No |
| Typical use case | Content moderation | Chat history synchronization |
Pre-delivery callbacks
The following figure shows how the pre-delivery callbacks work.
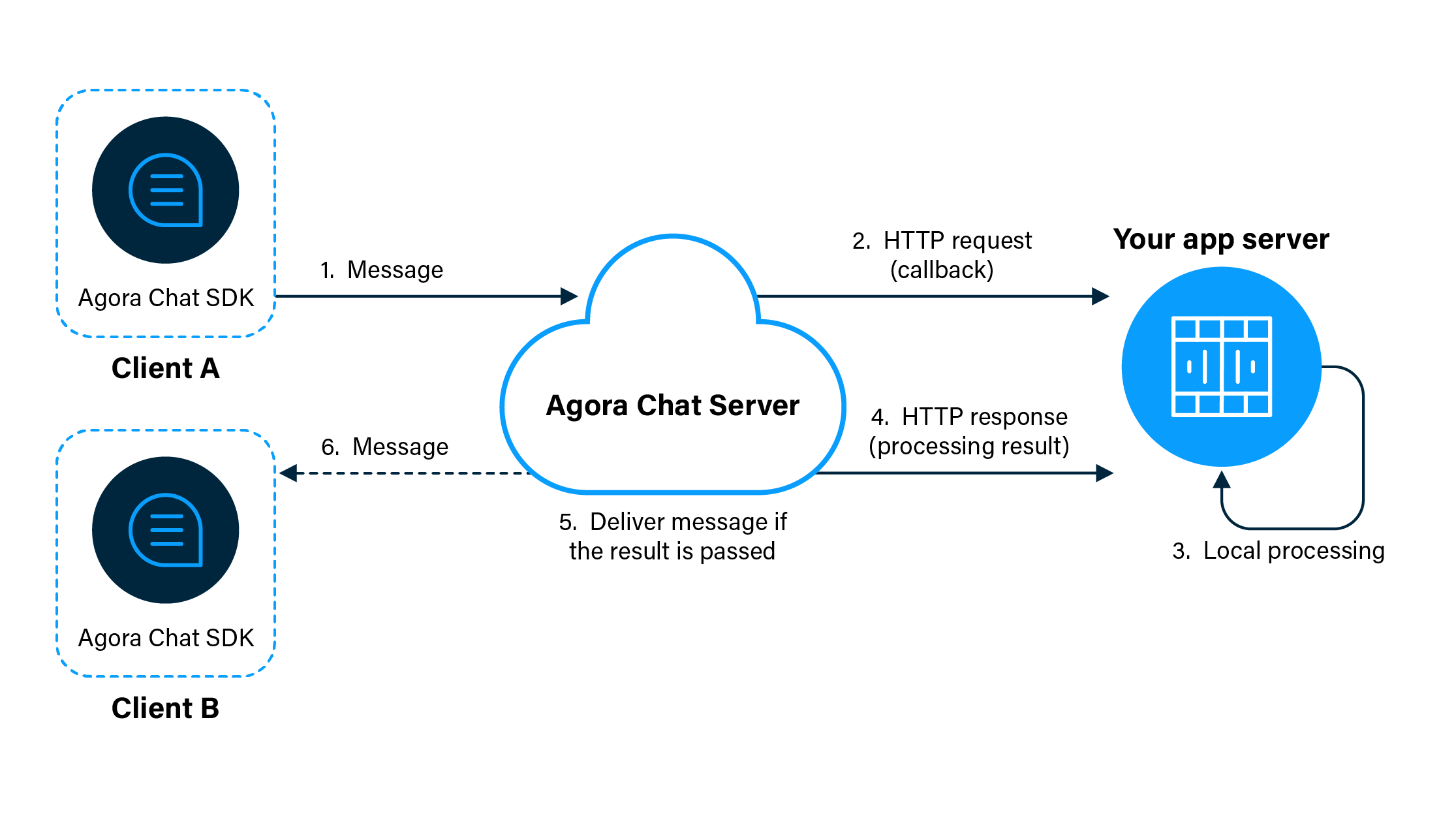
As shown in the figure, the workflow of pre-delivery callbacks is as follows:
- The Chat server receives a message from Client A.
- The Chat server sends an HTTP request that contains the information of the message to your app server.
- Your app server processes the received data and gets a result of whether the message delivery is passed or rejected.
- Your app server sends the processing result in the form of HTTP response to the Chat server.
- The Chat server receives the HTTP response and decides if the message delivery is passed.
- If the message delivery is passed, the Chat server delivers the message to Client B.
Post-delivery callbacks
As shown in the figure, the workflow of post-delivery callbacks is as follows:
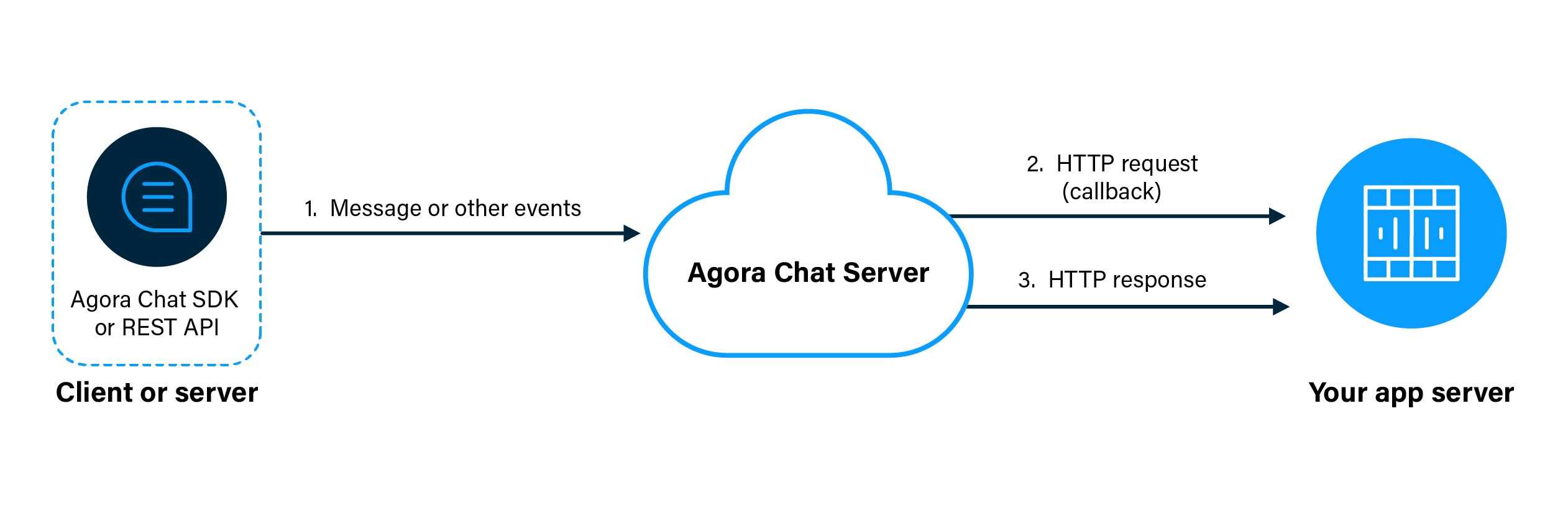
As shown in the figure, the workflow of post-delivery callbacks is as follows:
- The Chat server receives a message or other event from a client or server.
- The Chat server sends an HTTP request that contains the information of the message or event to your app server.
- Your app server sends an HTTP response to the Chat server to indicate that the callback is received.
Prerequisites
To use the HTTP callbacks, you must meet the following requirements:
- You have an Agora project with Chat enabled.
- You understand the API call frequency limit as described in Limitations.
- The HTTP callback feature is not enabled by default. To use this feature, you need to subscribe to the Pro or Enterprise pricing plan and enable it in Agora Console.
You must contact support@agora.io to disable this feature as this operation will delete all the relevant configurations.
Configure callback rules
To receive the HTTP callbacks, you need to configure rules for the pre- or post-delivery callbacks in Agora Console.
-
Log in to Agora Console and find your project on the Project Management page, then click the edit button.
-
Find Chat on the project editing page, and click Configure.
-
Click Add Target Url in the Real-time Callback section on the configuration page.
-
To add a rule for pre-delivery callbacks, fill the following fields under the pre send tab and then click Save.
- Rule Name: Enter a name for the rule. Under one project, each rule must have a unique name.
- Chat Type: Select the types of chat this rule applies to.
- Message Type: Select the types of messages this rule applies to.
- Timeout: (Optional) Specify the time (in ms) that the Chat server should wait for the HTTP responses. The default value is 200 ms. If the reponse times out, the Chat server continues with the fallback action.
- Fallback Action: (Optional) Select the action of the Chat server when the HTTP response times out or returns errors. The default option is pass.
- Target Url: Enter the URL of your app server for receiving the pre-delivery callbacks. Supports both HTTP and HTTPS URLs.
- Rejection Behaviour: (Optional) Set whether to notify the message sender when their message is rejected. The default option is to not notify the message sender.
-
To add a rule for post-delivery callbacks, fill the following fields under the post send tab and then click Save.
- Rule Name: Enter a name for the rule. Under one project, each rule must have a unique name.
- Callback Service: Select the types of chat or events this rule applies to.
- Message Type: Select the types of messages this rule applies to.
- Message Status: Select whether this rule applies to chat or offline messages, or both.
- To synchronize the chat history on your own server, select chat messages. All messages sent by the users are chat messages, regardless of the online status of the message receiver.
- To push message notifications, select offline messages. Messages sent to an offline user are counted as offline messages.
- Target Url: Enter the URL of your app server for receiving the post-delivery callbacks. Supports both HTTP and HTTPS URLs.
The rules take effect immediately.
Note the following for the rule configurations:
- By default, you can add four rules for the pre- and post-delivery callbacks in total. To extend the limit, contact support@agora.io.
- The rule configuration only supports message events. To receive notifications of other events, contact support@agora.io.
- If you have set both pre- and post-delivery callbacks, and a message is rejected after the pre-delivery callback returns, the post-delivery callbacks are not triggered.
Next steps
To enhance the security of the callbacks, Chat includes a signature in the request body of each callback. You can verify the signature to check whether the callbacks are sent from the Chat server.
To verify the signature in a callback, do the following:
-
Retrieve the following information:
-
The callback ID, which is the callId paramater in the request body of the callback.
-
The secret assigned to the callback rule. You can find this value on the Chat configuration page in Agora Console.
-
The callback timestamp, which is the timestamp parameter in the request body of the callback.
-
-
Calculate the MD5 value of the concated string of the callback ID, the secret, and the callback timestamp.
-
Check if the calculated value equals to the secret parameter in the request body. If yes, the callback is sent by Chat.
Reference
This sections provides the details of the HTTP requests and responses.
HTTP request
When certain events occur in your Chat app, the Chat server sends HTTP POST requests with JSON payloads. The character encoding is UTF-8. The Content-Type field in all HTTP request headers is application/json.
HTTP response
For the pre-delivery callbacks, the Chat server accepts HTTP responses that contain a JSON body as in the following example:
valid: Boolean. Whether the message is valid according to the processing result on your app server:- true: The message is valid and the Chat server should deliver the message.
- false: The message is invalid and the Chat server should reject the message.
code: String. Custom information.
For the post-delivery callbacks, ensure that the response content does not exceed 1,000 characters.
Retry logic
-
For pre-delivery callbacks, if your app server does not return the HTTP code 200 and the valid status, the Chat server does not resend the callback and takes the fallback action specified by the applicable rule.
-
For post-delivery callbacks, the Chat server records a notification failure and tries resending the callback once in one of the following situations:
- Your server does not respond in 60 seconds.
- The HTTP status code received from your server is not 200.
If the second try fails, the Chat server stops trying.
If 90 notification failures occur in 30 seconds, the corresponding callback rule is automatically turned off for five minutes. (To query and resend the missed notifications, use the Callback APIs.)